 Ella Verbs
Ella VerbsHow to conjugate Escapar in Spanish
To escape Regular AR Verb
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Indicative tenses of Escapar
- Escapar in the Indicative Present
- Escapar in the Indicative Preterite
- Escapar in the Indicative Imperfect
- Escapar in the Indicative Present Continuous
- Escapar in the Indicative Informal Future
- Escapar in the Indicative Future
- Escapar in the Indicative Conditional
- Escapar in the Indicative Present Perfect
- Escapar in the Indicative Past Perfect
- Escapar in the Indicative Future Perfect
- Escapar in the Indicative Conditional Perfect
- Subjunctive tenses of Escapar
- Imperative tenses of Escapar
- Downloadable cheat sheet (PDF)
- Practice Escapar conjugations (free mobile app)
Introduction
Escapar is the Spanish verb for "to escape". It is a regular AR verb. Read on below to see how it is conjugated in the 18 major Spanish tenses!
Similar verbs to escapar include: escabullirse, escaparse, fugar, fugarse, huir, zafar.
| Item | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Infinitive | escapar | to escape |
| Past participle | escapado | escaped |
| Gerund | escapando | escaping |
Indicative Tenses of Escapar
Escapar in the Indicative Present
The Indicative Present of escapar is used to talk about situations, events or thoughts that are happening now or in the near future. It is also used to talk about facts and truths. For example, "escapo", meaning "I escape".
In Spanish, the Indicative Present is known as "El Presente".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | escapo | I escape |
| Tú | escapas | you escape |
| Ella / Él / Usted | escapa | s/he escapes, you (formal) escape |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | escapamos | we escape |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | escapáis | you (plural) escape |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | escapan | they escape |
Back to top
Escapar in the Indicative Preterite
The Indicative Preterite of escapar is used to talk about actions completed in the past, at a specific point in time. For example, "escapé", meaning "I escaped".
In Spanish, the Indicative Preterite is known as "El Pretérito Indefinido".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | escapé | I escaped |
| Tú | escapaste | you escaped |
| Ella / Él / Usted | escapó | s/he escaped, you (formal) escaped |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | escapamos | we escaped |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | escapasteis | you (plural) escaped |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | escaparon | they escaped |
Back to top
Escapar in the Indicative Imperfect
The Indicative Imperfect of escapar is used to describe regular and repeated actions that happened in the past and descriptions of things you used to do. For example, "escapaba", meaning "I used to escape".
In Spanish, the Indicative Imperfect is known as "El Pretérito Imperfecto".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | escapaba | I used to escape |
| Tú | escapabas | you used to escape |
| Ella / Él / Usted | escapaba | s/he used to escape, you (formal) used to escape |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | escapábamos | we used to escape |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | escapabais | you (plural) used to escape |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | escapaban | they used to escape |
Back to top
Escapar in the Indicative Present Continuous
The Indicative Present Continuous of escapar is used to talk about something that is happening continuously or right now. For example, "estoy escapando", meaning "I am escaping".
In Spanish, the Indicative Present Continuous is known as "El Presente Progresivo".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | estoy escapando | I am escaping |
| Tú | estás escapando | you are escaping |
| Ella / Él / Usted | está escapando | s/he is escaping, you (formal) are escaping |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | estamos escapando | we are escaping |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | estáis escapando | you (plural) are escaping |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | están escapando | they are escaping |
Back to top
Escapar in the Indicative Informal Future
The Indicative Informal Future of escapar is used to talk about something that will happen in the future, especially in the near future. For example, "voy a escapar", meaning "I am going to escape".
In Spanish, the Indicative Informal Future is known as "El Futuro Próximo".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | voy a escapar | I am going to escape |
| Tú | vas a escapar | you are going to escape |
| Ella / Él / Usted | va a escapar | s/he is going to escape, you (formal) are going to escape |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | vamos a escapar | we are going to escape |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | vais a escapar | you (plural) are going to escape |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | van a escapar | they are going to escape |
Back to top
Escapar in the Indicative Future
The Indicative Future of escapar is used to talk about something that will happen in the future. For example, "escaparé", meaning "I will escape".
In Spanish, the Indicative Future is known as "El Futuro Simple".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | escaparé | I will escape |
| Tú | escaparás | you will escape |
| Ella / Él / Usted | escapará | s/he will escape, you (formal) will escape |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | escaparemos | we will escape |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | escaparéis | you (plural) will escape |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | escaparán | they will escape |
Back to top
Escapar in the Indicative Conditional
The Indicative Conditional of escapar is used to talk about something that may happen in the future, hypothesis and probabilities. For example, "escaparía", meaning "I would escape".
In Spanish, the Indicative Conditional is known as "El Condicional Simple".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | escaparía | I would escape |
| Tú | escaparías | you would escape |
| Ella / Él / Usted | escaparía | s/he would escape, you (formal) would escape |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | escaparíamos | we would escape |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | escaparíais | you (plural) would escape |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | escaparían | they would escape |
Back to top
Escapar in the Indicative Present Perfect
The Indicative Present Perfect of escapar is used to describe actions that started recently (in the past) and are still happening now or things that have been done recently. For example, "he escapado", meaning "I have escaped".
In Spanish, the Indicative Present Perfect is known as "El Pretérito Perfecto".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | he escapado | I have escaped |
| Tú | has escapado | you have escaped |
| Ella / Él / Usted | ha escapado | s/he has escaped, you (formal) have escaped |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | hemos escapado | we have escaped |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | habéis escapado | you (plural) have escaped |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | han escapado | they have escaped |
Back to top
Escapar in the Indicative Past Perfect
The Indicative Past Perfect of escapar is used to talk about actions that happened before another action in the past. For example, "había escapado", meaning "I had escaped".
In Spanish, the Indicative Past Perfect is known as "El Pretérito Pluscuamperfecto".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | había escapado | I had escaped |
| Tú | habías escapado | you had escaped |
| Ella / Él / Usted | había escapado | s/he had escaped, you (formal) had escaped |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | habíamos escapado | we had escaped |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | habíais escapado | you (plural) had escaped |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | habían escapado | they had escaped |
Back to top
Escapar in the Indicative Future Perfect
The Indicative Future Perfect of escapar is used to talk about something that will have happened in the future after something else has already happened. For example, "habré escapado", meaning "I will have escaped".
In Spanish, the Indicative Future Perfect is known as "El Futuro Perfecto".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | habré escapado | I will have escaped |
| Tú | habrás escapado | you will have escaped |
| Ella / Él / Usted | habrá escapado | s/he will have escaped, you (formal) will have escaped |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | habremos escapado | we will have escaped |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | habréis escapado | you (plural) will have escaped |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | habrán escapado | they will have escaped |
Back to top
Escapar in the Indicative Conditional Perfect
The Indicative Conditional Perfect of escapar is used to talk about something that would have happened in the past but didn’t due to another action. For example, "habría escapado", meaning "I would have escaped".
In Spanish, the Indicative Conditional Perfect is known as "El Condicional Perfecto".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | habría escapado | I would have escaped |
| Tú | habrías escapado | you would have escaped |
| Ella / Él / Usted | habría escapado | s/he would have escaped, you (formal) would have escaped |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | habríamos escapado | we would have escaped |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | habríais escapado | you (plural) would have escaped |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | habrían escapado | they would have escaped |
Back to top
Subjunctive Tenses of Escapar
Escapar in the Subjunctive Present
The Subjunctive Present is used to talk about situations of uncertainty, or emotions such as wishes, desires and hopes. It differs from the indicative mood due to the uncertainty of the events which are being spoken about. For example, "escape", meaning "I escape".
In Spanish, the Subjunctive Present is known as "El Presente de Subjuntivo".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | escape | I escape |
| Tú | escapes | you escape |
| Ella / Él / Usted | escape | s/he escapes, you (formal) escape |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | escapemos | we escape |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | escapéis | you (plural) escape |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | escapen | they escape |
Back to top
Escapar in the Subjunctive Imperfect
The Subjunctive Imperfect is used to speak about unlikely or uncertain events in the past or to cast an opinion (emotional) about something that happened in the past. For example, "escapara", meaning "I escaped".
In Spanish, the Subjunctive Imperfect is known as "El Imperfecto Subjuntivo".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | escapara | I escaped |
| Tú | escaparas | you escaped |
| Ella / Él / Usted | escapara | s/he escaped, you (formal) escaped |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | escapáramos | we escaped |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | escaparais | you (plural) escaped |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | escaparan | they escaped |
Back to top
Escapar in the Subjunctive Future
The Subjunctive Future is used to speak about hypothetical situations, and actions/events that may happen in the future. For example, "escapare", meaning "I will escape".
In Spanish, the Subjunctive Future is known as "El Futuro de Subjuntivo".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | escapare | I will escape |
| Tú | escapares | you will escape |
| Ella / Él / Usted | escapare | s/he will escape, you (formal) will escape |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | escapáremos | we will escape |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | escapareis | you (plural) will escape |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | escaparen | they will escape |
Back to top
Escapar in the Subjunctive Present Perfect
The Subjunctive Present Perfect is used to describe past actions or events that are still connected to the present day and to speak about an action that will have happened by a certain time in the future. For example, "haya escapado", meaning "I have escaped".
In Spanish, the Subjunctive Present Perfect is known as "El Pretérito Perfecto de Subjuntivo".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | haya escapado | I have escaped |
| Tú | hayas escapado | you have escaped |
| Ella / Él / Usted | haya escapado | s/he has escaped, you (formal) have escaped |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | hayamos escapado | we have escaped |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | hayáis escapado | you (plural) have escaped |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | hayan escapado | they have escaped |
Back to top
Escapar in the Subjunctive Past Perfect
The Subjunctive Past Perfect is used to speak about hypothetical situations, and actions/events that occurred before other actions/events in the past. For example, "hubiera escapado", meaning "I had escaped".
In Spanish, the Subjunctive Past Perfect is known as "El Pretérito Pluscuamperfecto de Subjuntivo".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | hubiera escapado | I had escaped |
| Tú | hubieras escapado | you had escaped |
| Ella / Él / Usted | hubiera escapado | s/he had escaped, you (formal) had escaped |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | hubiéramos escapado | we had escaped |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | hubierais escapado | you (plural) had escaped |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | hubieran escapado | they had escaped |
Back to top
Escapar in the Subjunctive Future Perfect
The Subjunctive Future Perfect is used to speak about something that will have happened if a hypothetical situations occurs in the future. For example, "hubiere escapado", meaning "I will have escaped".
In Spanish, the Subjunctive Future Perfect is known as "El Futuro Perfecto de Subjuntivo".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | hubiere escapado | I will have escaped |
| Tú | hubieres escapado | you will have escaped |
| Ella / Él / Usted | hubiere escapado | s/he will have escaped, you (formal) will have escaped |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | hubiéremos escapado | we will have escaped |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | hubiereis escapado | you (plural) will have escaped |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | hubieren escapado | they will have escaped |
Back to top
Imperative Tenses of Escapar
Escapar in the Imperative Affirmative
The Imperative Affirmative is used to give orders and commands, to tell someone to do something. For example, "escape", meaning "(to you formal) escape!".
In Spanish, the Imperative Affirmative is known as "El Imperativo Afirmativo".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | - | - |
| Tú | escapa | (to you) escape! |
| Ella / Él / Usted | escape | (to you formal) escape! |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | escapemos | let's escape! |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | escapad | (to you plural) escape! |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | escapen | (to you plural formal) escape! |
Back to top
Escapar in the Imperative Negative
The Imperative Negative is used to give orders and commands, telling someone not to do something. For example, "no escape", meaning "(to you formal) don't escape!".
In Spanish, the Imperative Negative is known as "El Imperativo Negativo".
| Pronoun | Spanish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | - | - |
| Tú | no escapes | (to you) don't escape! |
| Ella / Él / Usted | no escape | (to you formal) don't escape! |
| Nosotras / Nosotros | no escapemos | let's not escape! |
| Vosotras / Vosotros | no escapéis | (to you plural) don't escape! |
| Ellas / Ellos / Ustedes | no escapen | (to you plural formal) don't escape! |
Back to top
Downloadable cheat sheets
Download and print a cheat sheet of Escapar Spanish conjugation tables in image or PDF format:
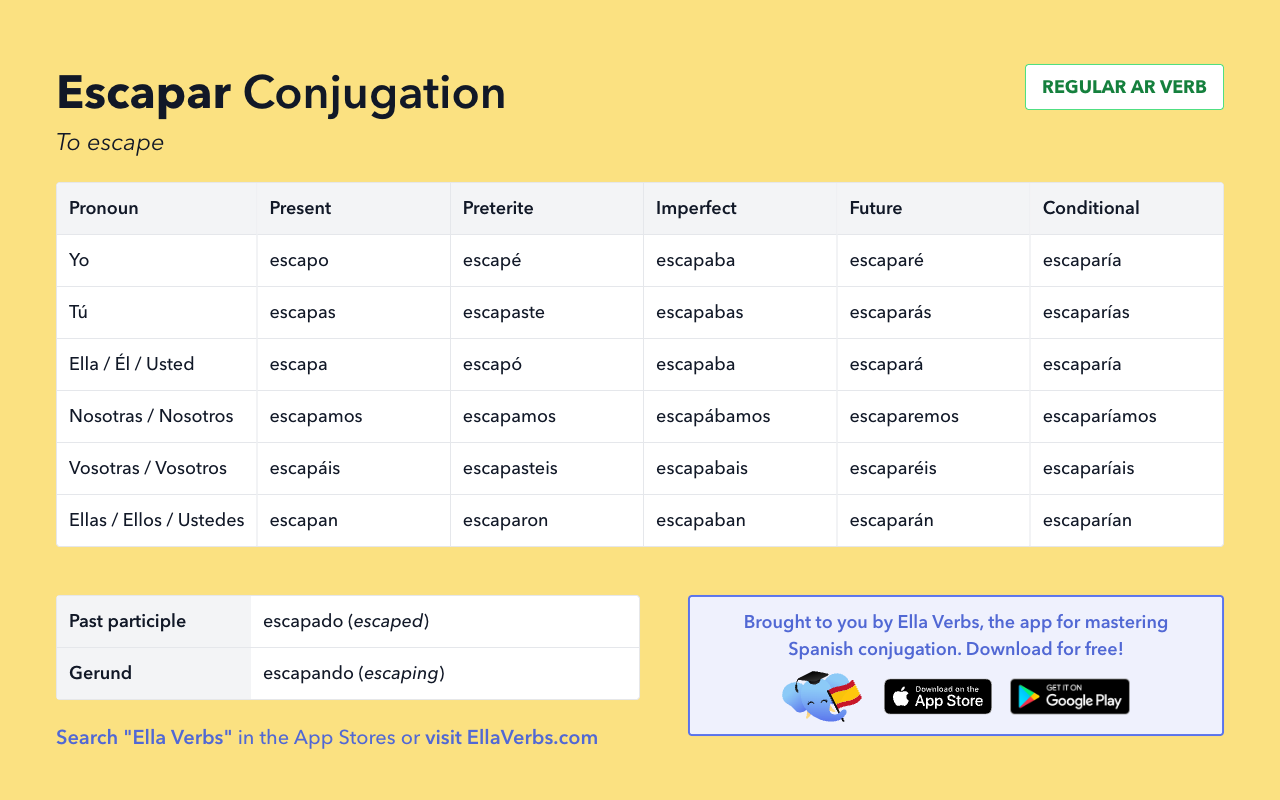
Back to top
Practice Escapar conjugations (free mobile & web app)
Get full conjugation tables for Escapar and 2,300+ other verbs on-the-go with Ella Verbs for iOS, Android, and web.
We also guide you through learning all Spanish tenses and test your knowledge with conjugation quizzes. Download it for free!
Back to top
About Ella Verbs
👋 Hola! We built Ella Verbs to help people (and ourselves!) master one of the hardest parts of Spanish – verb conjugation. It guides you through learning all tenses in an easy-to-follow way, giving you levels of bite-sized lessons and fun quizzes. Here is a 6 minute overview of all of the app's features:
It has changed a lot over the 6+ years we have been working on it, but the goal remains the same – to help you master Spanish conjugation! You can download and try it for free, and, if you do, please send any and all feedback our way!
- Jane & Brian
Back to top
Want to explore other verb conjugations?
Why not check out Escaparse – to escape or see the complete list of verbs here.
Back to top
Escapar: to escape
Remove the mystery behind Spanish conjugation with Ella Verbs
- Learn how to conjugate (not just memorize)
- Discover & focus on your weaknesses
- Interactive quizzes that you actually learn from
- Free to try, and free forever for those who cannot afford it.
